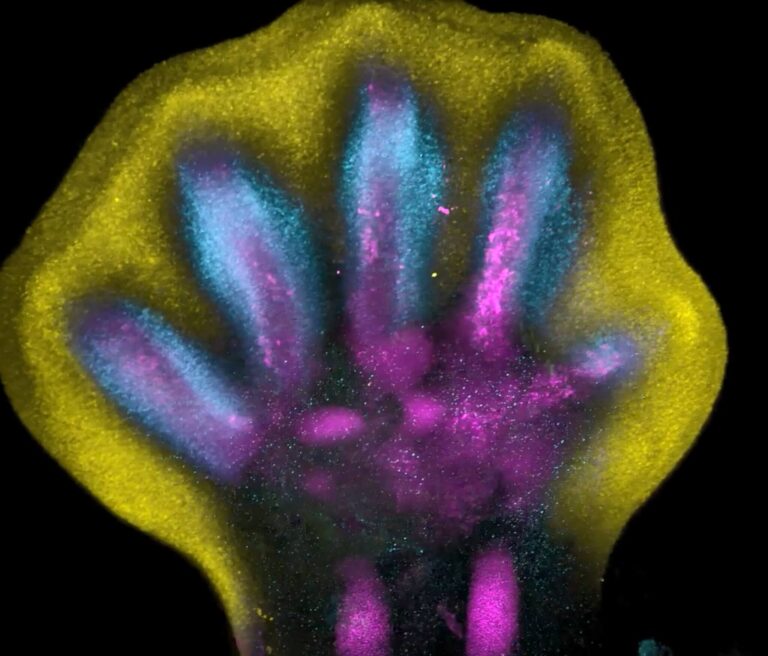
HINXTON, United Kingdom — Scientists have unveiled groundbreaking insights into human limb growth, offering new insights into the advanced processes behind their formation. Not like outward development, human fingers and toes emerge from a bigger foundational bud, with intervening cells receding to reveal the digits. Roughly seven weeks into cell growth, an orchestrated means of cell loss of life reveals the distinct shapes of fingers and toes.
This discovery is a part of a pioneering effort to create a spatial cell atlas of all the developing human limb, capturing these processes for the primary time. Utilizing particular tissue staining, researchers had been capable of observe how cell populations prepare themselves into the rising patterns of digits.
The findings have important implications for treating muscle-related disorders and accidents and will affect the prognosis and remedy of congenital limb syndromes. Carried out as a part of the Human Cell Atlas initiative, which goals to map each human cell kind, the examine concerned researchers from the Wellcome Sanger Institute, Solar Yat-sen College, EMBL’s European Bioinformatics Institute, and different collaborators. They utilized superior single-cell and spatial applied sciences to chart the mobile panorama of the early human limb, pinpointing cell areas.

Printed within the journal Nature, the atlas serves as an overtly accessible useful resource, detailing the limbs’ fast growth throughout early formation. It additionally reveals new connections between developmental cells and a few congenital limb syndromes, similar to brachydactyly (quick fingers) and polysyndactyly (additional digits).
Initially, limbs begin as undefined cell pouches on the physique’s sides, remodeling into anatomically advanced, recognizable limbs with fingers and toes after eight weeks. This fast, exact mobile orchestration is prone to disturbances, resulting in limb variations, among the most typical beginning syndromes, affecting about one in 500 births worldwide.
Whereas earlier research on limb growth primarily used mouse and chick fashions, their relevance to human growth was unsure. Nevertheless, technological developments now allow the exploration of human limb formation’s early phases.
On this examine, scientists analyzed tissues from five to nine weeks of development, tracing particular gene expression patterns that form limbs. They recognized sure genes, whose disruption is linked to particular limb syndromes, similar to brachydactyly and polysyndactyly. Moreover, the analysis confirmed similarities in limb growth between people and mice.
Total, these insights supply a complete understanding of human limb growth and maintain the potential to affect congenital limb syndrome prognosis and remedy.

“Many years of learning mannequin organisms established the premise for our understanding of vertebrate limb growth. Nevertheless, characterizing this in people has been elusive till now, and we couldn’t assume the relevance of mouse fashions for human growth, says Professor Hongbo Zhang, the senior writer of the examine from Solar Yat-sen College, in a media release.
“What we reveal is a extremely advanced and exactly regulated course of. It’s like watching a sculptor at work, chiseling away at a block of marble to disclose a masterpiece. On this case, nature is the sculptor, and the result’s the unimaginable complexity of our fingers and toes.”
“For the primary time, we’ve got been capable of seize the outstanding means of limb development right down to single-cell decision in house and time, provides Dr. Sarah Teichmann, senior writer of the examine from the Wellcome Sanger Institute and co-founder of the Human Cell Atlas.
“Our work within the Human Cell Atlas is deepening our understanding of how anatomically advanced constructions kind, serving to us uncover the genetic and mobile processes behind wholesome human growth, with many implications for analysis and healthcare. As an example, we found novel roles of key genes MSC andPITX1 which will regulate muscle stem cells. This might supply potential for treating muscle-related issues or accidents.”
South West Information Service author Dean Murray contributed to this report.
You may additionally be interested by:
