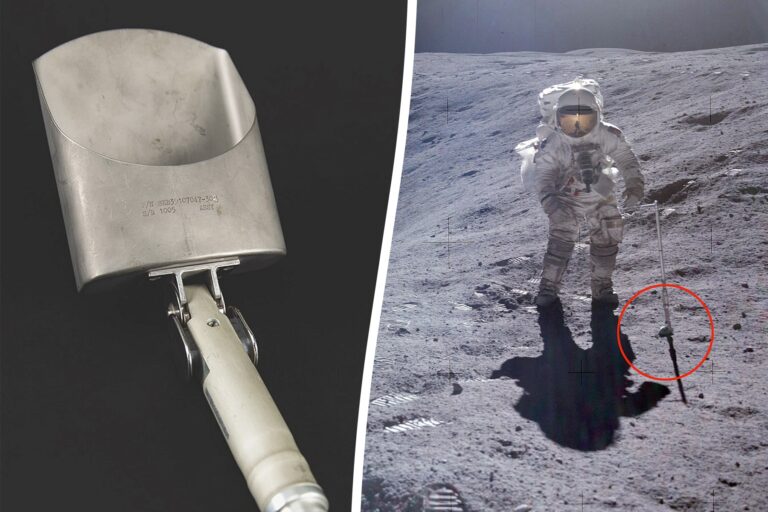
Should you’re wanting so as to add a outstanding piece of area exploration historical past to your mantel, you’re in luck. The “moon rock scoop” that was instrumental in NASA’s Apollo 16 mission is about to be auctioned.
This iconic device, used extensively by Lunar Module Pilot Charlie Duke and Commander John Younger, is anticipated to usher in over $824,000. It comes from Duke’s private assortment of mission mementos.
Known as a shovel, the device was formally designated on the Apollo 16 stowage listing as “Scoop, Giant Adjustable.” It performed an important position through the historic 1972 Apollo 16 mission, the fifth during which people landed on the Moon.
Younger and Duke spent over 20 hours on conducting three separate moonwalks through the mission. The astronauts trusted this instrument to gather 211 kilos (95.8 kilograms) of lunar samples, highlighting its vital position within the mission’s success. There’s considerable video footage and pictures documenting using this scoop all through the mission.
Among the many many lunar samples procured utilizing this device, the standout is “Large Muley,” a 26-pound (11.7 kg) moon rock. This rock is essentially the most large specimen collected all through the entire Apollo program.
“I needed to, one time, choose up a rock that was most likely the dimensions of a watermelon, and I couldn’t choose it up with one hand,” Duke remembers in an interview forward of the public sale (see video under). “So I put the shovel down and leaned on in direction of it, and rolled this rock up my aspect with my proper hand, and was in a position to roll it up my leg and cradle it like a bit child, and take it again to the Lunar Module.”
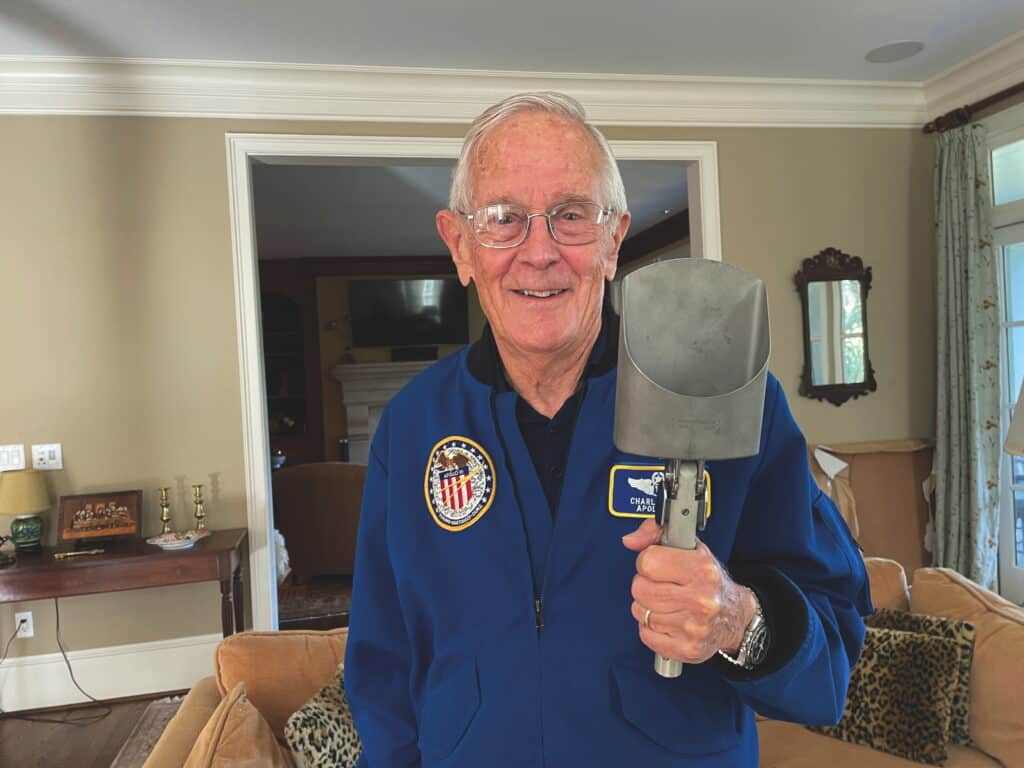

Because the Lunar Module pilot of Apollo 16, Duke earned the excellence of changing into the tenth particular person and the youngest at 36 years and 201 days, to set foot on the Moon.
The design of the news was superior for its period. It featured a pole section and spring-loaded buttons, permitting it to rotate to 180°, 45°, and 90° positions. This function made it straightforward for astronauts to dig, scoop, and scrape.
Seen abrasions on the news’s blade bear witness to its heavy use in lunar pattern assortment.
“What distinguishes this scoop is its distinctive standing as a lunar artifact that made its way back to Earth. Among the many profitable Apollo lunar touchdown missions, just one different lunar scoop (from Apollo 14) was returned,” Boston-based RR Auctions writes. “The remaining had been left on the moon to save lots of weight for the return flight, together with the deal with extension for this very scoop.”
“From the second Charlie Duke offered this scoop to us, I acknowledged its significance as crucial lunar artifact we’ve ever had,” provides Bobby Livingston, Government Vice President at RR Public sale.
This scoop can be accessible on the Area Exploration and Aviation public sale hosted by RR Auction, concluding on October 19.
Information and figures from the Apollo 16 mission
Apollo 16 was the fifth mission during which people landed on the Moon and the penultimate mission of NASA’s Apollo program. Listed here are the important thing particulars in regards to the Apollo 16 mission:
Launch Date: Apollo 16 was launched on April 16, 1972, from the Kennedy Area Heart in Florida.
Command Module: The Command Module was named “Casper,” and it was the spacecraft used for the return journey to Earth.
Lunar Module: The Lunar Module, named “Orion,” was used for the moon touchdown.
Crew:
- John W. Younger (Commander): This was his fourth spaceflight, and he later went on to fly the Area Shuttle.
- Charles M. Duke Jr. (Lunar Module Pilot): He and Younger explored the Moon’s floor collectively.
- Thomas Okay. Mattingly II (Command Module Pilot): He stayed in lunar orbit aboard the Command Module whereas Younger and Duke descended to the lunar floor.
Lunar Touchdown Web site: The chosen web site for touchdown was the Descartes Highlands, a area not beforehand visited. Scientists believed this space would supply proof of lunar volcanic exercise, although it was later decided that the formation was because of affect occasions, not volcanic exercise.
Lunar Floor Actions: Younger and Duke spent over 20 hours on extravehicular actions (EVAs), conducting three separate moonwalks. They collected samples, arrange experiments, and drove the Lunar Roving Automobile (LRV) to discover extra distant places.
Lunar Samples: The crew collected about 211 lbs (95.5 kg) of lunar samples, together with rocks, core samples, and soil.
Scientific Experiments: Amongst different devices, the Apollo Lunar Floor Experiments Bundle (ALSEP) was deployed, which included varied scientific devices to collect information from the Moon’s floor.
Return: The Lunar Module lifted off from the Moon on April 23, 1972, and rejoined the Command Module in lunar orbit. The crew then traveled again to Earth and splashed down within the Pacific Ocean on April 27, 1972.
Significance: Like different Apollo missions, Apollo 16 contributed considerably to our understanding of lunar geology and the Moon’s historical past. The mission demonstrated the utility of the LRV for extending the vary of human exploration on the lunar floor and confirmed that the Descartes area was primarily shaped from affect processes fairly than volcanism.
The Apollo program concluded with Apollo 17 in December 1972, marking the tip of human exploration of the Moon for a number of many years.
South West Information Service contributed to this report.


