WASHINGTON — You received’t have the ability to go to an everyday tattoo artist to get one of these ink. In a big scientific development, Johns Hopkins College engineers have designed nanoscale tattoos that may adhere to residing cells, bringing us one step nearer to real-time monitoring of particular person cell well being.
This revolutionary know-how introduces the power to position optical elements or electronics instantly on reside cells utilizing “tattoo” preparations. These preparations seamlessly match onto the cell’s wet and flexible exterior, very similar to a temporary tattoo on human skin.
“When you think about the place that is all going sooner or later, we want to have sensors to remotely monitor and management the state of particular person cells and the setting surrounding these cells in actual time,” says David Gracias, a professor of chemical and biomolecular engineering at Johns Hopkins College who led the event of the know-how, in a university release. “If we had applied sciences to trace the well being of remoted cells, we may possibly diagnose and deal with illnesses a lot earlier and never wait till the whole organ is broken.”
Gracias likens these mobile tattoos to barcodes or QR codes, functioning as a hyperlink between residing tissues and conventional sensors or digital supplies.
“We’re speaking about placing one thing like an digital tattoo on a residing object tens of occasions smaller than the pinnacle of a pin,” notes Gracias. “It’s step one in the direction of attaching sensors and electronics on reside cells.”

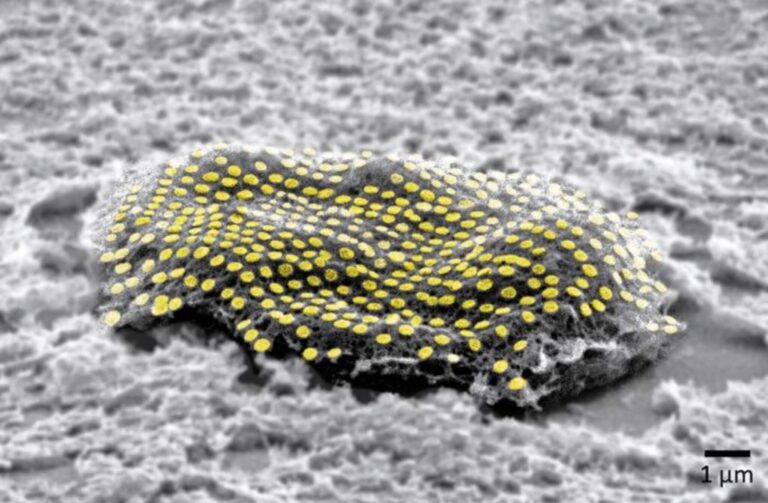
To make sure the tattoos stayed linked, they have been designed utilizing gold, a steel recognized for its conductive properties that forestall sign distortion. These have been then connected to fibroblasts, cells liable for tissue maintenance in humans. The bonding course of concerned molecular glues and an alginate hydrogel movie, a gel-like substance that dissolves after making certain the gold firmly sticks to the cell. The bond is additional strengthened because the glue reacts with a movie secreted by cells, generally known as the extracellular matrix.
Whereas previous research efficiently utilized hydrogels to stay nanotechnology onto human pores and skin and animal organs, the staff’s achievement lies in fixing nanowires and nanodots to particular person cells. This addresses the historic problem of integrating optical sensors and electronics with biological matter on such a microscopic stage.
“We’ve proven we will connect complicated nanopatterns to residing cells, whereas making certain that the cell doesn’t die,” says Gracias. “It’s an important consequence that the cells can reside and transfer with the tattoos as a result of there’s typically a big incompatibility between residing cells and the strategies engineers use to fabricate electronics.”
The strategic association of those dots and wires is pivotal. For the know-how to successfully monitor organic information, the sensors and wiring have to be methodically positioned, akin to digital chip configurations.
“That is an array with particular spacing,” explains Gracias, “not a haphazard bunch of dots.”
The examine is printed within the journal Nano Letters.
